At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What are Eukaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic cells are a type of cell more complex than their counterparts, prokaryotes. Prokaryotes include the simplistic bacteria and archaea, while eukaryotes make up all fungi, animals, plants, and protists such as amoeba. Together with viruses and other snippets of genetic material, prokaryotes and eukaryotes make up all known terrestrial life.
Eukaryotic cells are characterized by internal membranes and a strong cytoskeleton. A cytoskeleton is a framework of proteins, such as actin and keratin, which help hold a cell together and differentiate its organelles. Eukaryote means "true nut," referring to the fact that eukaryotic cells possess an internal nucleus whereas prokaryotes (meaning "before nut") do not. In prokaryotes, the genetic material floats freely in the cytoplasm (cellular blood), while in eukaryotes, it is protected in a special nucleus. Eukaryotic DNA is organized into chromosomes whereas prokaryotic DNA is not.

Eukaryotes are more recent in the history of life than prokaryotes, and the typical eukaryotic cell is larger than a typical prokaryotic cell. Whereas prokaryotic life emerged as long as 3.8 billion years ago, eukaryotes only evolved between 1.6 and 2.1 billion years ago. One of the first eukaryotic organisms was red algae, whose form has barely changed in 1.2 billion years.

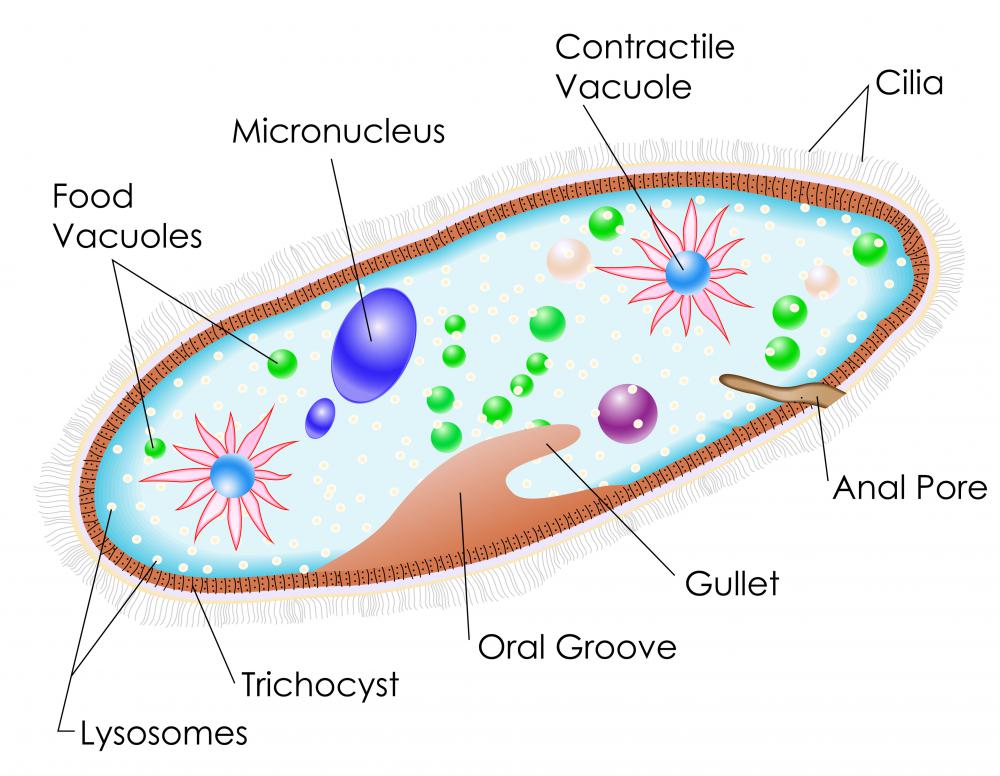
Eukaryotes have organelles, or cellular organs, while prokaryotes basically don't. A characteristic organelle found in almost all eukaryotes is the mitochondria, known as the power station of the cell. It is thought that the mitochondria was once a free-moving prokaryote which cooperated so closely with the early eukaryotes that they became a part of the same organism in a process known as endosymbiotic attachment. Other organelles include the ribosome, vesicles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, flagella, vacuoles, lysosomes, and centrioles. All organelles have special functions and are usually enclosed in their own lipid membranes.

Eukaryotic cells have a much greater diversity in their structure than prokaryotic cells. For instance, plant cells are very different from animal cells. Plant cells have a hard outer shell called a cell wall, while animal cells just have a flexible cell membrane. Plant cells also possess a special organelle, the chloroplast, which engages in photosynthesis.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discussion Comments
It is interesting to note that the mitochondrion, the energy generator of the eukaryotic cell, is felt to be a "eukaryotic endosymbiont," deriving perhaps from a primitive bacteria whose function has been usurped by more complex life form.
The mitochondrial DNA in eukaryotic cells is different from the nuclear DNA and, as it is strictly matrilineal, it's origins can be traced backward from their origin. A nice demonstration of evolution!
Eukaryotic cells are often designed to deal with unwanted prokaryotic cells, in the form of bacterium. Prokaryotic cells in the human system are unwelcome guests, and can be harmful if they are not dealt with properly. Even more harmful are viruses, which infect eukaryotic cells and spread like parasites via intercellular signals.
@FitzMaurice
Scientists are beginning to realize how truly complex this basic building block of life is. It follows and executes a rigid set of actions which are determined by the DNA coding, which varies depending on the cell and location in the body. The entire DNA and genome of a given species is made diverse by the various different codings they inherit from their parents.
It would seem that the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is somewhat like a prokaryote. The DNA is encapsulated within, but floats freely about there. This hub of the cell, the nucleus, is what controls the transmission of protein signals in the form of DNA transmission to other parts of the cell, and to the function of the collective cellular body.
Prokaryotes came before eukaryotes. In the history of evolution, it would be interesting to postulate if eukaryotes will one day evolve into an even more complex and intricately effective form than that which they currently possess.
Post your comments