At EasyTechJunkie, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Telegraph?
A telegraph is a machine that is used for transmitting messages in the form of electrical impulses, which can be converted into data. A message sent this way is called a telegram or cablegram, while someone who operates a machine is known as a telegrapher. Telegraphy was a major mode of communication from the middle of the 1800s until well into the 1900s, before ultimately being supplanted by inventions like the telephone and the Internet.
The earliest version of the telegraph was developed in the late 1700s, primarily as a thought exercise. This early draft only existed on paper, but it laid the groundwork for various incarnations of the device that appeared in the early 1800s. With the development of the electromagnet, Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail were able to develop and patent a reliable electric system in 1837.

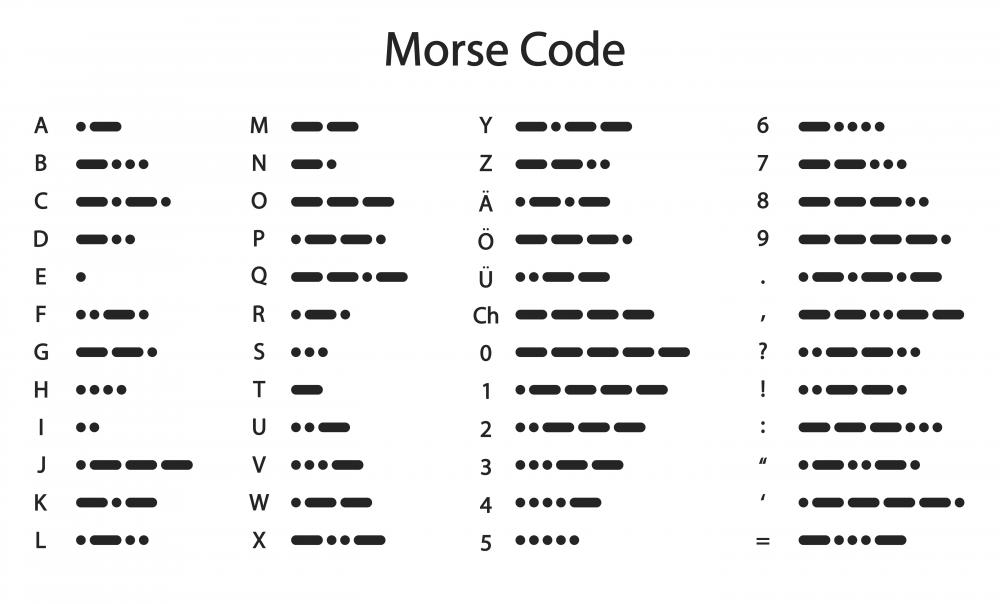
Morse is often credited with being the inventor of the telegraph, but this is not the case. Many other inventors had patented various versions of the machine before Morse, and history strongly suggests that Alfred Vail was the scientific brains of the operation. Morse popularized the device, however, and developed a workable, easily learned alphabet that could be transmitted using it.

Originally, the machines had to be connected through a series of wires in order to exchange messages. The operator would key a message in the Morse alphabet, and the receiving machine on the other side would register the message in the form of clicks made by one bar that struck another. By listening to the pattern of clicks, the receiving operator could hear the message and transcribe it before passing it on to the recipient.

In the late 1800s, wireless telegraphy began to emerge, and messages were transmitted over the radio waves. This marked a drastic change in the system, allowing people to rapidly transmit messages in areas without cables, and enabling things like ship-to-ship communication. Wireless telegraphy, or radiotelegraphy, also laid the groundwork for later methods of communication.

The telegraph is largely obsolete now. One famous company, Western Union, sent its last telegram in 2006, and many other companies have stopped offering telegram services because consumer demand has fallen radically. Telegrams are generally regarded as interesting curiosities, as is the peculiar language used in them. Because transmitting the signal is painstaking, operators developed their own shorthand to make transmission more rapid.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:











Discussion Comments
My wife and I have heard the distinct clicking sounds characteristic of Morse code. Is it possible for the human ear to "hear" the clicking of telegraphy without use of any type of electronic device?
The telegraph was a great thing for the people back then and I think it would be kind of cool to use it today.
@Iluviaporos - I can't believe that Western Union doesn't do telegraphs anymore. It makes me kind of sad, the same way I felt when Kodak stopped developing film.
I remember when my grandmother died several people sent their condolences by telegraph and I've seen it done in weddings as well. I remember being taught the code for SOS when I was a child, and always felt like if I was trapped somewhere it might save my life one day.
It's definitely the passing of an era and I didn't even realize that it had happened.
@Mor - I've lived in a town in a developing country where we didn't have personal phones, there was no cell phone coverage and no internet. Most of the time we got news by mail and if we were lucky, someone might call us on the local phone, which we had to pay to use and which had a bunch of guys on bicycles on standby to fetch whoever was receiving the call.
It was about twelve hours to the nearest city and if our one phone died we had no means of instant contact with the "outside world". Having lived in those conditions I can tell you that the telegraph must have been an absolute marvel to those folk. The same way that cellphones were once a marvel and USENET was once a marvel. Being able to instantly communicate with people who aren't right next to us should never be taken for granted.
@georgew - I'm not sure what information you want, but that was the phrase that Samuel Morse used on the first telegraph he sent over the single wire telegraph system in 1844. He chose that phrase because one of his financial backers picked it, but really I think it's quite a clever phrase to send. It must have seemed like a miracle back then to be able to send messages like that from one side of the country to the other.
People don't think of Morse Code as being a digital innovation but it is just that. While the telegraphs lines might have carried an analog signal, the very nature of how a telegraph uses an on or off audible tone is a digitalization of the text it is carrying.
I think this is a point that is often missed when discussing antique technologies such as this.
wanting information regarding a round the world east telegraph with "what hath God wrought" It was sent, (1807 time) to Asmara and then to San Francisco and then to Boston(?) The message produced a tape with holes punched. Guess the time period mid to late 1800's
Post your comments