At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Phospholipid Bilayer?
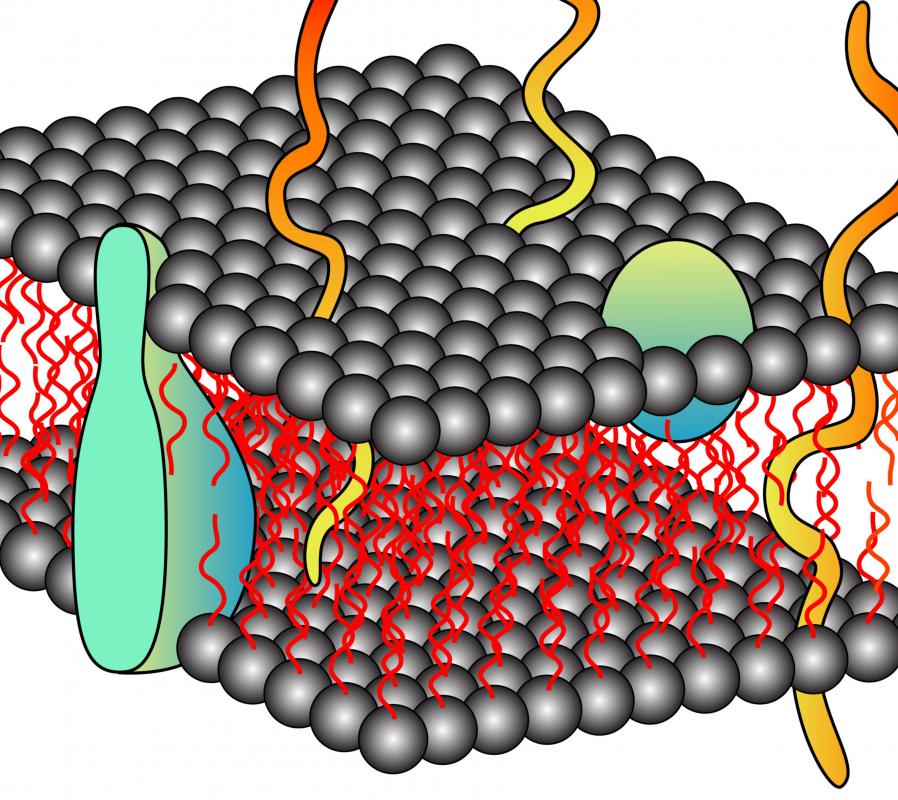
The phospholipid bilayer is the two-layer membrane that surrounds many types of plant and animal cells. It's made up of molecules called phospholipids, which arrange themselves in two parallel layers, forming a membrane that can only be penetrated by certain types of substances. This gives the cell a clear boundary, and keeps unwanted substances out. Though the phospholipid bilayer works well most of the time, it can be damaged, and some types of unwanted substances can bypass it.
Characteristics

Phospholipids have two ends, one of which is hydrophilic, or attracted to water, and one of which is hydrophobic, or repelled by water. Since the inside of cells is mostly water, and the area outside of cells is mostly water, these molecules arrange themselves into two layers, with the hydrophilic ends of each layer pointing outwards, and the hydrophobic ones pointing inwards. Since they are lipids, or fats, they are not broken down by water, and are solid enough not to let large molecules pass through without the help of another substance. Smaller molecules, like oxygen and carbon dioxide, can pass through easily on their own, but larger ones like sodium, magnesium, or water can't.

The inside of the membrane is also fluid, and allows sphingolipids, cholesterol or sterols, and proteins to move in it. Sphingolipids help protect the outside of the cell, and the cholesterols and sterols help stabilize the phospholipid bilayer in animal and plant cells, respectivelly. Though this is essential for cells to have enough stability, too much cholesterol can make them rigid, which is dangerous if they are part of an artery that needs to be flexible to let blood flow. The proteins are used to transport substances in or out of the cell through the bilayer and provide places for certain substances to bind to the outside of the cell.
Purpose

One of the main purposes of the phospholipid bilayer are to provide structure to a cell, which it does because of the natural arrangement of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends of the phospholipids, and with the stabilizing cholesterol and sterols. Its other purpose is to regulate the types of substances that can go into the cell or connect with it, which it does in several ways using proteins. Some types of protein extend from the top of the membrane so that they can be used to identify the cell or to make a place for certain substances to bind to it.

There are also several types of proteins that can form channels or tunnels for certain substances to pass through. Some are just open all the time to specific types of molecules, while others are more like gates, and need energy to open and close. This is called active transport, and can be done both to bring materials in and out of the cell. It's commonly used with substances like sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Problems
The phospholipid bilayer is fairly stable, but it can be damaged by strong solvents and oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Also, some types of harmful substances, like viruses, can bypass the membrane or trick the cell into absorbing them. Other viruses, notably Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) have a specialized membrane that they can fuse to that of a cell and then attack it.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discussion Comments
@bananas: Look up 'emergence' and 'evolution'...
And than some people say there is no God, all of this complicated formations and processes happened just by accident.
If not for the phospholipid bilayer membrane, our cells would have almost no protection against the world outside. Funny how much something we cannot see affects our functions on so many levels of life.
Post your comments